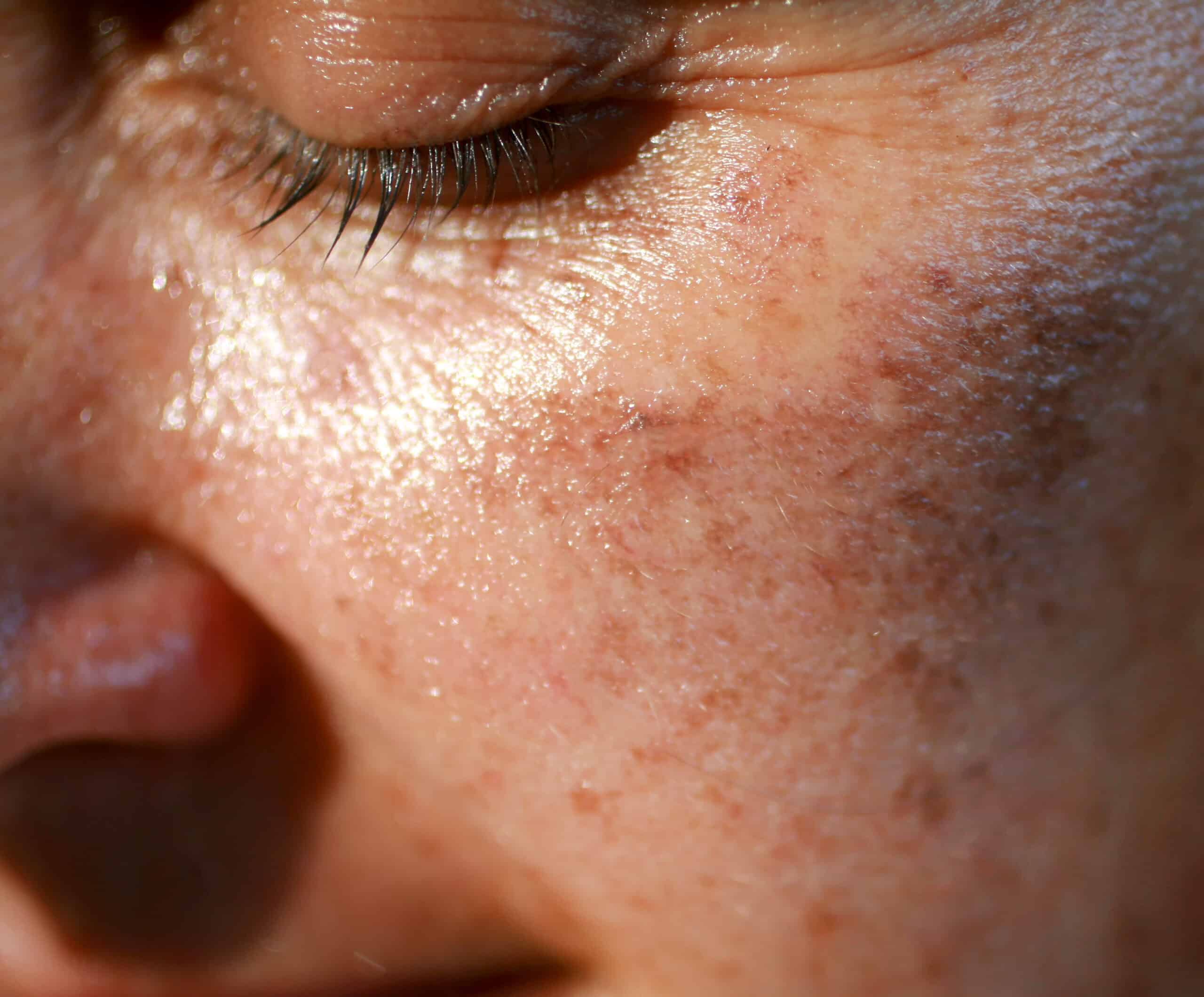
Melasma is a complex form of skin pigmentation characterized by brown, gray, or blue-toned patches, typically appearing on the face. Often triggered by hormonal changes, sun exposure, or genetic factors, melasma can be persistent and challenging to treat. For those wondering how to treat melasma with skin therapies, understanding the science behind the condition and exploring the latest non-invasive treatments is key to achieving visible, lasting improvement.
What is melasma treatment and how it works?
Melasma treatments are designed to regulate melanin production and lighten the discolored patches without damaging surrounding skin. These therapies work by targeting the melanocytes responsible for Skin Pigmentation Treatment in Dubai(علاج التصبغات في دبي) production, reducing inflammation, and enhancing skin turnover.
The approach may involve topical ingredients, chemical peels, laser treatments, microneedling, or light-based therapies. These options help to break down excess pigment and promote a brighter, more uniform complexion. Since melasma can be deep-rooted, multiple sessions and maintenance are usually necessary to sustain results.
Importance of treating melasma early:
Melasma often worsens with prolonged UV exposure or hormonal fluctuation, which is why early and consistent treatment is vital. Addressing it promptly offers the following benefits:
-
Prevents pigment from deepening into the dermis
-
Minimizes the chance of recurrence through skin barrier support
-
Restores even tone, enhancing overall facial aesthetics
-
Helps manage emotional and social discomfort linked to hyperpigmentation
-
Enhances the absorption and performance of other skincare products
Skin therapies for melasma not only target discoloration but also contribute to healthier, more resilient skin in the long run.
Types of skin therapies for melasma:
Topical treatments
These are typically the first step for mild to moderate melasma:
-
Hydroquinone alternatives: Kojic acid, arbutin, and azelaic acid help fade pigment gradually
-
Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant that brightens and protects against UV damage
-
Niacinamide: Regulates melanin transfer and reduces inflammation
-
Tranexamic acid: A newer brightening agent that works on vascular components of melasma
Consistency and sun protection are essential to maximize results.
Chemical peels
Superficial chemical peels can speed up cell turnover and fade pigmentation:
-
Glycolic acid peels: Break down surface pigment and stimulate collagen
-
Salicylic acid: Ideal for combination or oily skin types
-
Lactic acid: Hydrates while gently exfoliating
-
TCA (trichloroacetic acid): Used in low concentrations for more stubborn pigment
Peels should be spaced out and customized based on skin sensitivity and melasma depth.
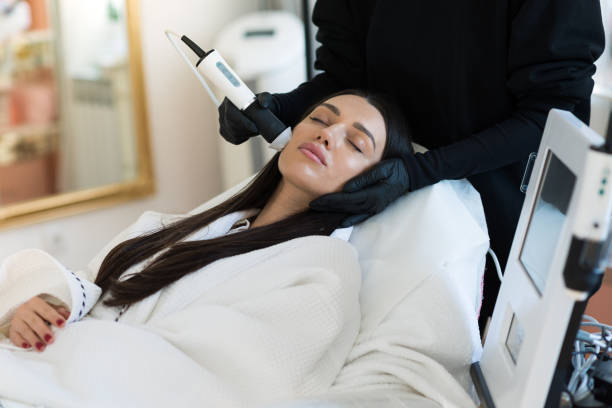
Laser and light-based therapies
These treatments must be used cautiously, as melasma can worsen if the skin is over-stimulated:
-
Q-switched lasers: Target excess melanin with minimal heat damage
-
Fractional lasers: Encourage controlled dermal remodeling
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Works best for epidermal pigmentation
-
Low-fluence laser toning: A gentle, repetitive method that minimizes risk of rebound pigmentation
Choosing the correct laser and frequency is critical to avoid adverse effects.
Microneedling and combination therapies
-
Microneedling boosts skin renewal and enhances the delivery of brightening serums
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can be combined for anti-inflammatory effects
-
Combination approaches involving microneedling with vitamin C or tranexamic acid can produce notable improvements over time
Such therapies are ideal for patients with mixed-type melasma (epidermal and dermal involvement).
Preparation before melasma treatment:
Skin preparation improves treatment absorption and reduces complications. Key steps include:
-
Begin using brightening serums and mild exfoliants 1–2 weeks before in-clinic treatments
-
Discontinue retinoids or other irritants 3–5 days in advance
-
Avoid waxing or threading on treatment areas before procedures
-
Maintain daily sunscreen application, even indoors
-
Perform a patch test for new actives
-
Stay well-hydrated and follow a calming skincare routine
A well-prepped skin barrier helps tolerate treatment better and enhances recovery.
Aftercare following melasma therapies:
Aftercare plays a crucial role in preventing post-inflammatory pigmentation and maintaining results:
-
Avoid sun exposure for at least one week post-treatment
-
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen SPF 50+ every 2–3 hours
-
Use gentle moisturizers and hydrating mists
-
Refrain from using makeup or active ingredients (retinoids, acids) for 48 hours
-
Do not exfoliate or scrub until skin has fully healed
-
Stay away from heat sources like saunas or hot showers temporarily
Post-treatment care is essential to reduce relapse and enhance the long-term fading of melasma.
Who is the ideal candidate for melasma therapies?
Not everyone responds to treatment in the same way, but ideal candidates typically:
-
Have persistent melasma triggered by sun exposure or hormonal shifts
-
Do not have active acne or infections in the treatment area
-
Are committed to sun protection and consistent skin routines
-
Have realistic expectations regarding gradual improvement
-
Are willing to follow a customized combination of topical and in-clinic treatments
Those with deeper skin tones can also benefit from skin therapies when approached with caution and customized plans.
How to choose the right treatment approach?
With various options available, choosing the right treatment for melasma depends on several factors:
-
Determine whether the melasma is epidermal, dermal, or mixed
-
Start with gentle, non-invasive methods before progressing to aggressive therapies
-
Consider using combination treatments for better efficacy
-
Track your progress and adjust treatment plans based on skin response
-
Always prioritize daily sun protection to prevent relapse
-
Consult a skin professional to assess your skin type and tailor the best regimen
Melasma treatment is not one-size-fits-all—it requires personalization and patience.
Risks of treating melasma:
Though Skin Pigmentation Treatment(علاج التصبغات) are generally safe, certain risks must be acknowledged:
-
Irritation or peeling, especially from peels and topical acids
-
Rebound pigmentation if skin is overstimulated
-
Worsening melasma with inappropriate laser or heat-based therapies
-
Allergic reactions to actives or aftercare products
-
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation if aftercare is ignored
Mitigating these risks depends on professional guidance, patch testing, and strict sun protection.
Benefits of treating melasma with skin therapies:
Targeted skin therapies offer numerous advantages for melasma sufferers:
-
Visibly fades pigment patches and evens skin tone
-
Improves skin texture and brightness
-
Boosts self-confidence and appearance
-
Promotes long-term skin health and barrier function
-
Enhances overall skincare product absorption and effectiveness
-
Reduces need for heavy concealers or makeup
With proper treatment and maintenance, melasma can become significantly less noticeable over time.
Frequently asked questions:
Is melasma curable?
Melasma cannot be permanently cured, but it can be effectively managed and visibly improved with the right therapies and skincare routine.
How long does it take to see results?
Visible results may start to appear within 4–8 weeks for topical treatments and a few sessions for clinical therapies, depending on the severity.
Can melasma come back after treatment?
Yes, melasma can recur with sun exposure or hormonal changes, so maintenance is crucial.
Is laser treatment safe for melasma?
Some lasers are safe when used with proper technique and on the right skin types, but improper use can worsen pigmentation.
What ingredients should I avoid?
Avoid harsh exfoliants, alcohol-based products, and highly fragranced items that can irritate or inflame sensitive skin.
Conclusion:
If you’re searching for how to treat melasma with skin therapies, the journey starts with understanding your skin and choosing evidence-backed solutions. Whether through brightening topicals, controlled exfoliation, laser therapy, or microneedling, there are several paths to manage melasma effectively. By combining customized treatments with consistent sun protection and aftercare, melasma can be faded safely and gradually. The key is patience, consistency, and a strategy tailored to your unique skin profile. With time, the dull patches give way to clearer, brighter, and more radiant skin.





0 Comments